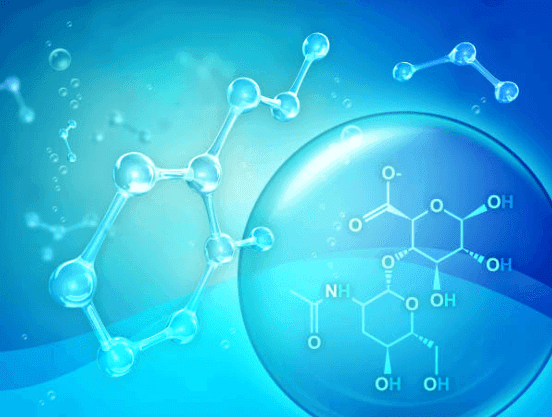
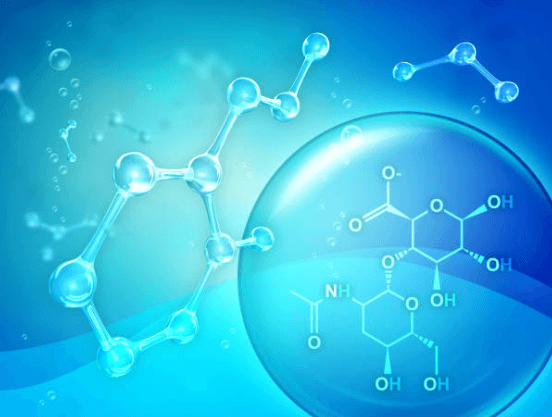
Common Name
Sodium hyaluronate; hyaluronan; HA
Historical and Traditional Uses:
Discovered in the vitreous body (1930s). Modern medical use spans ophthalmology (artificial tears, surgical adjuncts), rheumatology/orthopedics (intra-articular “viscosupplementation”), dermatology & aesthetics (topicals and dermal fillers), and wound care.
Chemical Composition:
-
The sodium salt of hyaluronic acid (HA), a non-sulfated linear glycosaminoglycan composed of repeating disaccharides D-glucuronic acid N-acetyl-D-glucosamine linked (1→4) between repeats. Molecular weight (MW) spans 10 kDa to 2 MDa depending on product.
-
Key properties: strong water binding/viscoelasticity, polyanionic character, receptor interactions that vary with chain length.
Pharmacological Properties:
- Biophysical: lubricates and cushions tissues (tear film, synovial fluid); maintains hydration; space-filling matrix.
- Topical skin effects: forms a hygroscopic film; low-MW fractions penetrate more effectively, improving hydration/elasticity and fine lines in trials.
Evidence-Based Uses and Benefits:
- Dry Eye Disease (artificial tears; ophthalmic gels/drops)
- Randomized/controlled data show sodium hyaluronate improves symptoms and ocular surface damage (e.g., reduced staining, better tear stability) versus baseline/placebo; benefit is class-consistent among artificial tears though head-to-head superiority over all comparators is not definitive.
- Skin Hydration / Fine Lines (topical)
- Double-blind RCT (J Drugs Dermatol 2011): 0.1% HA creams of various MWs improved skin hydration and elasticity; low-MW HA also reduced wrinkle depth versus placebo. Subsequent clinical and review articles support MW-dependent efficacy.
- Intra-articular Injection for Knee Osteoarthritis (viscosupplementation)
- Large 2022 BMJ systematic review/meta-analysis found small average pain reductions that did not reach minimal clinically important differences, with higher risk of adverse events than placebo;
AAOS 2021 guideline: does not recommend routine use of hyaluronic acid injections for knee OA. Use is center- and patient-specific after shared decision-making.
- Dermal Fillers (injectable, cross-linked HA)
- Widely used for soft-tissue augmentation. Most reactions are mild and transient; rare but serious events include vascular occlusion/necrosis (and, if peri-ocular, blindness), requiring urgent management (e.g., hyaluronidase, warmth, massage, antiplatelet/vasodilator algorithms).
Counter Indications:
- Ophthalmic drops: active ocular infection or hypersensitivity to components—defer until cleared.
- Intra-articular injections: active joint/skin infection, severe inflammatory flare, or known allergy to product components (some brands historically derived from avian sources). Follow local labeling.
- Dermal fillers: infection/inflammation at injection site, history of severe filler complications, or inability to access emergent management (hyaluronidase) in case of vascular compromise. Needle-free “hyaluron pens” are unsafe and not recommended by regulators.
Side Effects:
- Topical skin: generally well tolerated; occasional transient stinging or dermatitis from vehicle/excipients.
- Ophthalmic: transient blur, stinging; rare allergy.
- Intra-articular: post-injection pain/swelling (“pseudoseptic” flare), warmth; very rare infection. Overall effect size modest; weigh against cost and alternatives.
- Fillers: swelling, bruising, nodules; vascular occlusion is rare but vision-threatening if embolic treat immediately per protocols.
Drug Interactions:
- Systemic pharmacokinetic interactions: none clinically significant sodium hyaluronate is a local/structural biopolymer with minimal systemic absorption.
- Procedural interactions: for fillers, avoid concurrent procedures that increase bleeding/bruising risk (anticoagulants/antiplatelets, high-dose fish oil/garlic/ginkgo); these do not contraindicate but may increase bruising manage per clinician protocol. For intra-articular injections, standard anticoagulation precautions apply
Research and White Papers with Links:
1. Structure & biology: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10856924/ 2. Dry eye (ophthalmic): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11564544/ 3. Topical dermatology: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10078143/ 4. Knee OA injections: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6463231/ 5. Filler safety: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10659657/
Conclusions:
Sodium hyaluronate is a versatile, well tolerated biopolymer whose clinical value rests on local biophysical effects and MW-dependent biology: Strong evidence: ocular surface lubrication (dry-eye symptom relief) and topical skin hydration (with wrinkle-depth improvements in low-MW formulations). Controversial/limited: knee OA viscosupplementation major guidelines do not recommend routine use given small average benefit. Aesthetic injections: effective when performed by trained clinicians, but carry rare, serious risks requiring immediate recognition and treatment. Use quality controlled, appropriately formulated products, match MW/formulation to the indication, and ensure readiness to manage complications for any injectable use.
