Common Name
D-mannose, mannose
Parts Used
Purified D-mannose powder or capsules (manufactured from plant starches such as corn)
Native To
Naturally present in small amounts in some fruits (e.g., cranberry) and produced endogenously as part of human glycoprotein synthesis.
Historical and Traditional Uses:
D-mannose rose to popularity as a non-antibiotic strategy to prevent recurrent urinary tract infections (rUTIs) based on its ability to block adhesion of uropathogenic E. coli to the urothelium. Early small trials suggested benefit; a large, modern primary-care RCT did not confirm efficacy (see evidence below).
Chemical Composition:
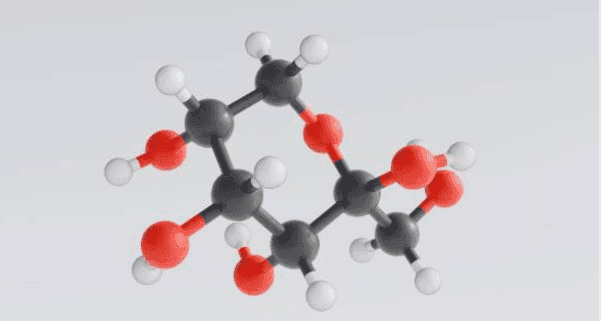
- Molecular formula: C₆H₁₂O₆ (C-2 epimer of glucose).
- Formulations:free sugar (powder/capsules); typical serving size 500–1,000 mg per capsule or 2 g per sachet.
Pharmacological Properties:
- Anti-adhesion: Uropathogenic E. coli express FimH, a type-1 fimbrial mannose-binding adhesin. High urinary levels of D-mannose competitively occupy FimH, reducing bacterial attachment to mannosylated receptors on urothelial cells.
- Pharmacokinetics: After oral intake, a portion of D-mannose is absorbed and excreted in urine, raising urinary mannose concentrations; extent depends on dose, urine volume, and timing of voiding. Human pilot work confirms urinary recovery after oral dosing.
Evidence-Based Uses and Benefits:
1. Prevention of recurrent UTIs (women)
- Large primary-care RCT (UK, 99 practices; n=598; 2 g daily for 6 months): No reduction in medically attended rUTIs vs placebo; secondary outcomes also negative. Authors conclude D-mannose should not be recommended for prophylaxis in this group.
- Earlier small trials (e.g., 2014 WJU): suggested fewer rUTIs with D-mannose vs no prophylaxis and results similar to nitrofurantoin; however, study limitations and later higher-quality evidence above supersede these findings.
- Systematic review (Cochrane 2022): evidence insufficient/very low certainty for prevention or treatment; called for robust placebo-controlled trials (addressed by 2024 RCT).
Guidelines: Contemporary guidance for rUTI focuses on behavioral measures, vaginal estrogen (post-menopause), methenamine hippurate, and (select cases) antibiotics; D-mannose is not recommended.
Bottom line: As of the latest high-quality evidence, routine D-mannose for rUTI prevention is not supported.
2) Treatment of acute UTI
- No convincing evidence that D-mannose treats active infection; antibiotics remain standard of care. (See NIHR evidence summary aligning with the RCT above.)
Counter Indications:
- Pregnancy & lactation: Insufficient high-quality safety data at supplemental doses—avoid routine use unless advised by a clinician.
- Diabetes/insulin resistance: D-mannose is a sugar; it is only partially metabolized, but monitor glucose if using regularly.
- Renal disease: Human safety data are limited; use caution in significant kidney impairment (historical high-dose animal signals and theoretical concerns).
Side Effects:
- Common (dose-related): bloating, loose stools/diarrhea.
- Uncommon: nausea, rare rash.
- Theoretical: at very high chronic doses, kidney strain has been raised as a concern (limited human data)
Drug Interactions:
- Clinically significant interactions: none well-documented.
- With antibiotics: sometimes co-taken for rUTI prevention; does not replace antibiotics for treatment.
- With antidiabetic drugs: monitor glycemic control if taking large or frequent doses.
Research and White Papers with Links:
- UTI prevention in women: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9427198/
- Early positive signals vs no prophylaxis/nitrofurantoin: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8944421/
- Mechanism (FimH–mannose adhesion): biophysical/biochemical literature: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7982833/
Conclusions:
D-mannose is a mannose sugar that can block E. coli FimH adhesion in vitro and raises urinary mannose after oral dosing. Yet, the best available clinical evidence a large, rigorous primary-care RCT (2 g/day for 6 months) found no prophylactic benefit for recurrent UTIs, and authoritative guidance does not recommend it for this purpose. If patients elect to try it, discuss the uncertain efficacy, potential GI side effects, and standard, guideline-supported alternatives (behavioral measures, vaginal estrogen, methenamine hippurate, or targeted antibiotic strategies when indicated).
